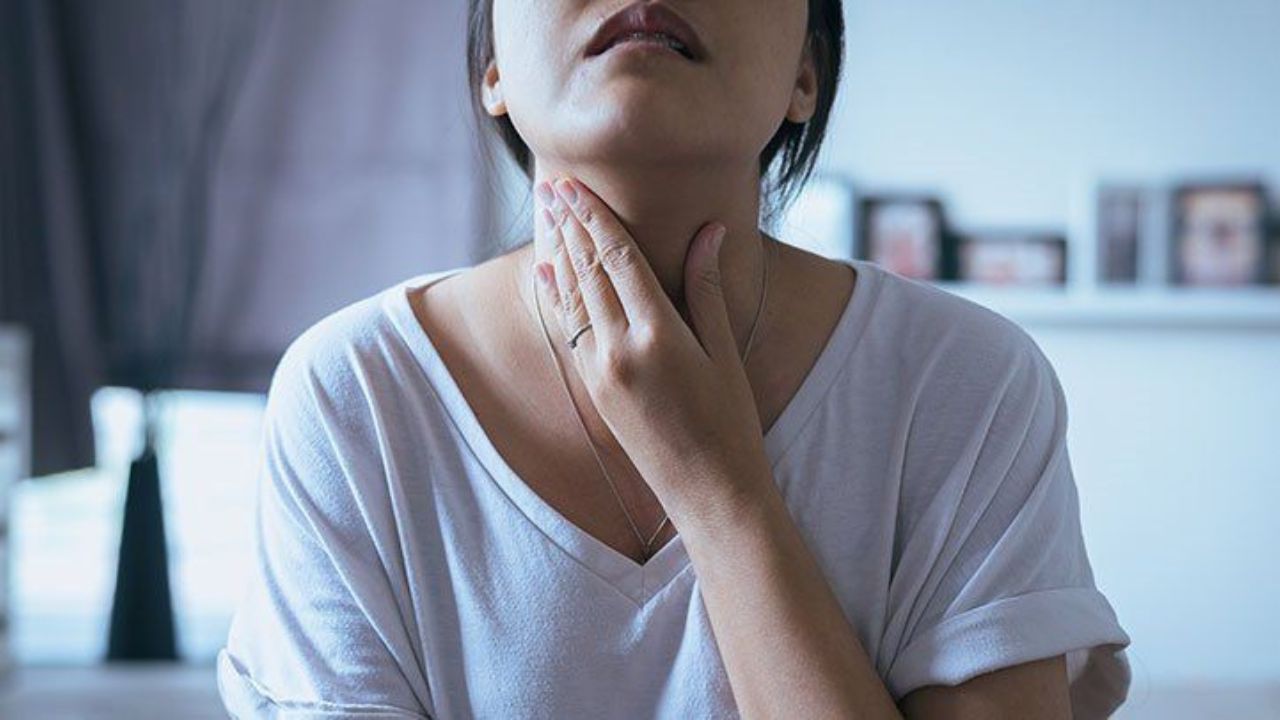
Tonsil stones, also known as tonsilloliths, are hard, calcified formations that develop in the crevices of the tonsils. While most people associate stones with kidneys or gallbladders, tonsil stones can also form in the throat. Many people are unaware of this condition, despite it being quite common. Tonsil stones develop from a buildup of food particles, mucus, and dead cells, which get trapped in the tonsil crypts. Over time, bacteria and viruses also start accumulating in these deposits, potentially leading to serious health concerns.
Where Do Tonsil Stones Form?
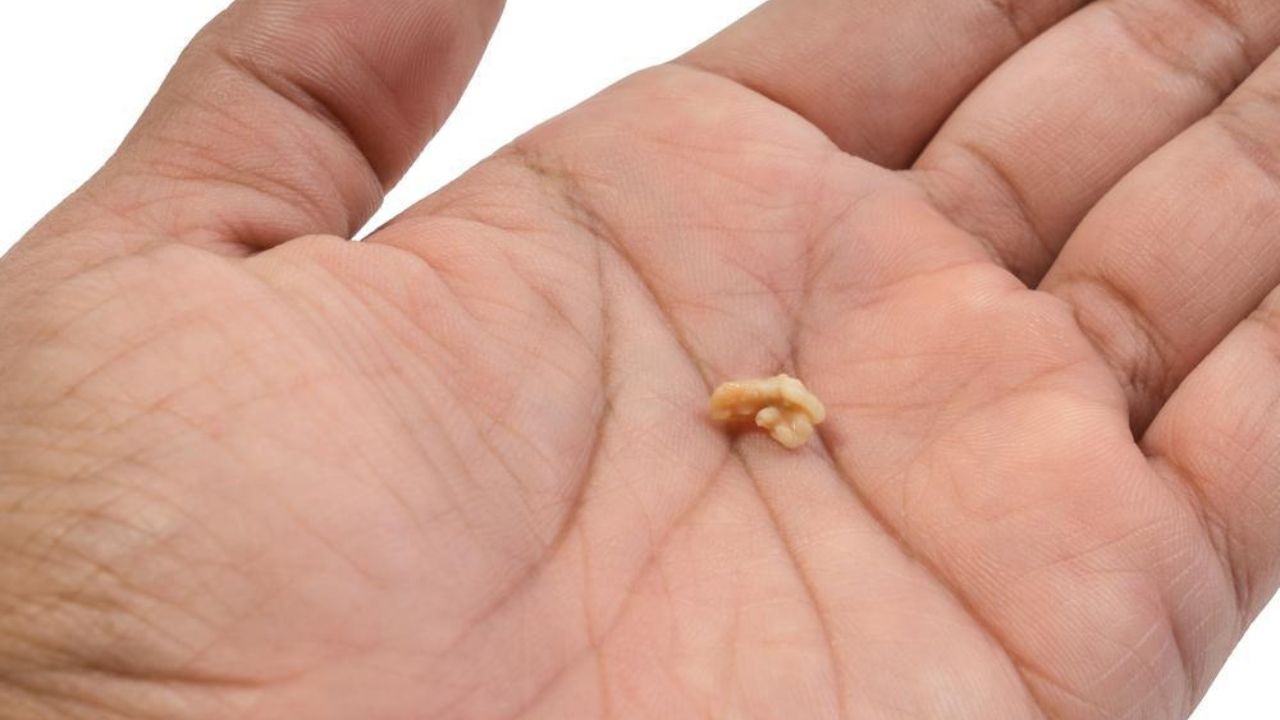
Tonsil stones typically form in the back of the throat, near the tonsils. They appear as small, white or yellowish lumps resembling grains of rice or pebbles. Initially, they may be as small as a pea, but if left untreated, they can grow larger, sometimes reaching the size of a golf ball in severe cases.
How Do Tonsil Stones Develop?
Doctors explain that the tonsils are located at the back of the throat, where they function as part of the body’s immune system. The surface of the tonsils contains folds and pockets, known as tonsil crypts. These crypts can trap food particles, dead cells, and bacteria, which over time harden into tonsil stones. This calcification process occurs due to the accumulation of minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium.
Symptoms of Tonsil Stones
Initially, tonsil stones may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as they grow in size, they can lead to various problems, including:
- Bad breath (Halitosis): One of the most common signs of tonsil stones is persistent bad breath, caused by bacteria thriving in the stone.
- Sore throat: Larger tonsil stones can cause irritation or pain in the throat.
- Difficulty swallowing: The presence of tonsil stones can make swallowing uncomfortable or even painful.
- Ear pain: Since the throat and ears share nerve pathways, tonsil stones can sometimes cause referred pain in the ears.
- Persistent cough: Some individuals may experience a chronic cough due to the irritation caused by tonsil stones.
- Feeling of something stuck in the throat: A sensation of obstruction or discomfort in the throat is a common complaint.
Health Risks Associated with Tonsil Stones
While tonsil stones are not usually harmful, ignoring them for a prolonged period can lead to complications. In rare cases, untreated tonsil stones can contribute to the development of tumors or other serious infections. If left unaddressed, they may also increase the risk of chronic tonsillitis or recurrent throat infections.
How to Prevent Tonsil Stones?
Preventing tonsil stones requires maintaining good oral hygiene. Here are some essential steps to reduce the risk of their formation:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing regularly can help eliminate food particles and bacteria from the mouth.
- Using an Antiseptic Mouthwash: Gargling with an antiseptic or saltwater solution helps reduce bacterial growth in the mouth and throat.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out food particles and debris, preventing buildup in the tonsil crypts.
- Good Dietary Habits: Avoiding sticky, sugary foods and maintaining a healthy diet can reduce the risk of tonsil stone formation.
- Removing Trapped Debris: Using a cotton swab or a water flosser can help remove small tonsil stones before they become problematic.
Treatment Options for Tonsil Stones
Home Remedies
- Gargling with Saltwater: This can help dislodge smaller tonsil stones and alleviate discomfort.
- Manual Removal: Some people gently remove small tonsil stones using a cotton swab or their fingers, but this should be done carefully to avoid injury.
- Hydration and Oral Hygiene: Keeping the mouth clean can prevent further buildup of debris and bacteria.
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics: In cases where bacterial infections are present, doctors may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial growth.
- Laser Tonsil Cryptolysis: This procedure smooths the tonsil crypts using laser technology, reducing the chances of debris getting trapped.
- Tonsillectomy: In severe cases where tonsil stones recur frequently and cause significant discomfort, surgical removal of the tonsils may be recommended.
When to See a Doctor?
If tonsil stones are causing persistent bad breath, difficulty swallowing, pain, or recurrent infections, it is advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of the condition.
Tonsil stones are a common but often overlooked health issue. While they may not always cause severe problems, they can lead to discomfort and bad breath. Practicing good oral hygiene and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing tonsil stones. If symptoms persist, seeking medical advice is the best way to ensure proper treatment and relief from this condition.


















